“`html
Comprehensive Guide to Chimpanzee Diet
The chimpanzee diet is a fascinating subject, shedding light on the complex feeding habits of these incredible primates. As researchers explore what do chimpanzees eat, we gain insights into their nutritional needs and dietary preferences in the wild. This guide will delve into various aspects of the chimpanzee’s feeding ecology, highlighting their main food sources and the impact of their environment on their diet. By understanding chimpanzee feeding habits, we can better appreciate how these intelligent creatures navigate their surroundings to meet their dietary needs.
Understanding Chimpanzee Feeding Habits
Chimpanzees are known for their diverse feeding habits, which are key to their survival in varied habitats. They exhibit a remarkable level of dietary flexibility, with an omnivorous diet that includes fruits, leaves, seeds, insects, and occasional meat. Understanding their chimpanzee nutrition helps in comprehending how they adapt their diet based on food availability and environmental changes. Their diets are heavily influenced by factors like seasonality and habitat type, making the study of chimpanzee food habits essential for conservation efforts. Observations of wild chimpanzees reveal their intricate foraging strategies, which include both solitary and social feeding behaviors.
Chimpanzee Primary Food Items
When examining the chimpanzee diet, a few primary food items stand out. Fruits are often the most preferred food source, contributing significantly to their energy intake. Different species of fruits, such as bananas, figs, and berries, play a crucial role in chimpanzee feeding habits, especially during fruiting seasons. Meanwhile, leaves also make up a substantial portion of their diet, providing fibers and essential nutrients. Additionally, the inclusion of insects contributes protein to their diet, showcasing the adaptability of chimpanzees and their awareness of nutritional requirements. The balance among these primary food items is key to maintaining optimal health and wellbeing in chimpanzees.
Chimpanzee Social Feeding
Social structures greatly influence chimps while foraging and consuming food. Chimpanzee social feeding often involves cooperation and competition among group members. They exhibit behaviors such as sharing and nurturing relationships centered around food, emphasizing the impact of social dynamics on feeding efficiency. Observations indicate that individuals often learn to forage effectively by observing their peers, indicating a high level of social learning in chimpanzees and dietary preferences. This social aspect is vital for their survival, as it enhances their ability to find and utilize food sources collectively.
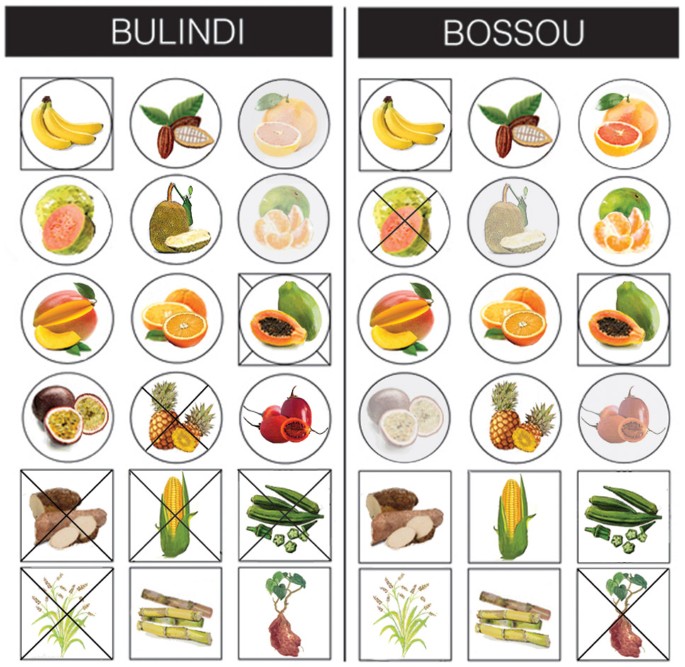
Diversity of Food Sources in Chimpanzees
The dietary patterns of chimpanzees are versatile, influenced by their habitat and forage availability. This section explores the range of food sources available, focusing on the significant role components play in their diet. Each food source is selected based on nutrient content and availability during different seasons, revealing the intricate relationship between chimpanzees and their environment. Studying their chimpanzee feeding ecology can shed light on many ongoing conservation challenges.
Fruits in Chimpanzee Diet
Fruits are pivotal in the chimpanzee diet, providing essential sugars and various vitamins. Based on nutritional value, mature chimpanzees prefer ripe fruit over unripe or dried options. Consequently, the nutritional value of fruits remains fundamental, dictating their energy accessibility and food choices. Ecologically, the availability of fruit—including various tropical fruiting trees—is influenced by seasonal weather changes, making it crucial for chimpanzees to adapt their foraging strategies. Fruiting seasons particularly create opportunities for wild chimpanzee diet variation, where communities congregate in fruit-rich areas, perfectly illustrating how food abundance affects their social structures.
Insects in Chimpanzee Diet
While fruits dominate their diet, insects also play a vital role, providing high-quality protein. Insects and their larvae represent a significant nutrient source for chimpanzees, known to display sophisticated foraging behavior in chimpanzees by using tools to extract insects from crevices. The significance of insects in chimpanzee diet cannot be overstated—these small creatures are essential for balancing their dietary intake, especially during seasons when fruits are scarce. Understanding these feeding techniques offers broader insights into the cognitive abilities of chimpanzees, highlighting how they adapt their behaviors for efficient foraging.
Chimpanzee Diet Variation and Preferences
Dietary preferences among chimpanzees showcase incredible diversity, reflecting both individual choices and social factors. Notably, preferences can vary widely by region, leading to differences in diet composition. Identifying various dietary shifts based on location and food availability informs us about the wider ecological impacts of chimpanzee feeding habits.
Dietary Shifts in Chimpanzees
Research has indicated that dietary shifts occur throughout the lifespan of chimpanzees. Younger individuals might favor fruits, but as they mature, their chimpanzee dietary needs can include more fibrous plant materials and insects to increase protein intake. Age-related dietary changes significantly influence their foraging behavior and social interactions. Observations suggest that older chimpanzees often serve as role models for younger ones, imparting knowledge about foraging efficiency and specific food types. This inter-generational learning underlies the social learning in chimpanzee feeding, enhancing the survival rates of younger members.
Factors Affecting Chimpanzee Diet
The dietary composition of chimpanzees is determined by various ecological factors. The interplay of seasonal patterns, environmental changes, and habitat loss collectively impacts the chimpanzee diet in the wild. Habitat fragmentation, often resulting from anthropogenic activity, significantly affects food availability and types, leading to difficult nutritional challenges for these primates. For instance, ongoing deforestation disrupts their natural foraging behavior, forcing chimpanzees to diversify more vigorously to locate adequate food supplies. Such changes inherently alter their feeding habits and contribute to the urgent need for effective conservation strategies focused on habitat preservation and restoration.
Chimpanzee Health and Diet
Understanding the link between chimpanzee health and diet is crucial, especially in the context of habitat degradation and changing environmental conditions. Healthy diets contribute to overall wellbeing, reducing vulnerability to diseases and promoting longer lifespans. In this section, we delve into how each food type influences genetic health and overall vitality in chimpanzees, thereby underscoring the need for maintaining diverse habitats.
Nutritional Analysis of Chimpanzee Diet
A detailed nutritional analysis of chimpanzee diet reveals that intake balancing is essential for preventing deficiencies. For instance, while fruit provides vital energy, micronutrients primarily sourced from leaves and insects ensure a well-rounded nutritional profile. Studies have identified common nutritional gaps, particularly among populations facing food scarcity due to habitat loss. This imbalance can contribute to increased disease susceptibility and lower reproductive success. Thus, understanding the intricate aspects of chimpanzee nutrition helps inform conservation efforts aimed at preserving both chimpanzee populations and their essential habitats.
Cultural Aspects of Chimpanzee Diets
Cultural behaviors surrounding food sharing and hunting vary widely among different chimpanzee groups. These behaviors often manifest specific practices around meat consumption in chimpanzees, such as collaborative hunting techniques carried out during group foraging excursions. Evidence shows that some populations of chimpanzees have developed unique preferences or techniques in obtaining food, making them subjects of interest in studies regarding chimpanzee intelligence and food. Documenting these cultural nuances not only enriches our understanding of their social lives but also emphasizes how such behaviors contribute to individual and community diets, as well as their success as a species.
Key Takeaways
- Chimpanzees exhibit a diverse diet that encompasses fruits, leaves, insects, and occasional meat.
- Their eating behaviors reflect social structures, with significant implications for their ecological roles.
- Seasonal availability of food influences foraging strategies and consequently affects their overall health and nutrition.
- Understanding these feeding habits is pivotal for developing effective conservation strategies for wild habitats.
FAQ
1. What are the primary food sources for chimpanzees?
The primary food sources for chimpanzees include fruits, leaves, insects, and occasionally meat. Their varied diet, characterized by chimpanzee dietary needs, allows them to adapt to different habitats and seasonal changes in food availability, ensuring adequate nutrition throughout their lives.
2. How does seasonal variation affect chimpanzee diet?
Seasonal variation plays a critical role in determining wild chimpanzee diet. During fruiting seasons, chimpanzees may rely heavily on ripe fruits, while in drier months, they may pivot towards leaves and other plant matter as their primary food source. This variability enhances their adaptability to environmental changes.
3. How do social behaviors influence chimpanzee feeding habits?
Social behaviors significantly influence chimpanzee eating behavior, as group dynamics affect their foraging efficiency and food sharing. Chimpanzees often learn food preferences and sophisticated foraging techniques from their peers, showcasing a high level of social learning in their feeding practices.
4. What health issues can arise from dietary imbalances in chimpanzees?
Dietary imbalances can lead to various health issues in chimpanzees, including nutritional deficiencies and increased susceptibility to diseases. Maintaining a balanced chimpanzee diet is crucial for fostering good health, especially in populations affected by habitat loss and changing food availability.
5. What impact does habitat loss have on chimpanzee diet?
Habitat loss severely affects the chimpanzee diet by reducing food availability and diversity. Deforestation and habitat fragmentation limit their access to essential food sources, leading to nutritional challenges and altering, in turn, their foraging behaviors and social structures.
“`