Effective Ways to Optimize Your Gastroparesis Diet for Better Digestion in 2025
Understanding the Gastroparesis Diet
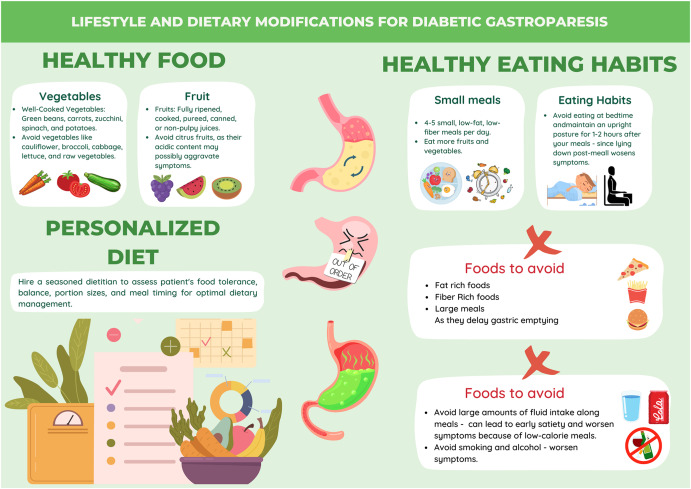
The **gastroparesis diet** is designed to help individuals manage the symptoms associated with delayed gastric emptying. This condition affects the ability to digest food properly, leading to various gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea and bloating. A well-planned **gastroparesis meal plan** can make a significant difference, ensuring that the body receives the necessary nutrients while keeping digestive discomfort to a minimum. Effective management often includes **small meals** throughout the day, focusing on **easy-to-digest foods** that provide nourishment without aggravating symptoms. Incorporating **high-protein meals** and **low-fat foods** can also be beneficial in supporting overall health and satiety.
Key Components of a Gastroparesis Meal Plan
When structuring a **gastroparesis meal plan**, it is essential to prioritize certain food groups and textures. Foods that are low in fiber are typically more manageable for digestion and fewer obstacles in the gastrointestinal tract. Incorporating **liquid diets** or drinkable meals can significantly ease the burden on the stomach. For instance, **fruit smoothies** filled with protein-rich ingredients or **vegetable broth** can provide essential nutrients while being gentle on the digestive system. Furthermore, maintaining **glycemic control** is crucial; selecting **nutrient-dense foods** that have a moderate impact on blood sugar levels helps in energy regulation throughout the day.
Recommended Food Textures and Frequencies
The texture of food plays an incredibly important role in a **gastroparesis diet**. Soft foods and blended ingredients are generally easier for the body to handle. Soft fruits, well-cooked vegetables, and pureed dishes should be staples in any **meal prep**. Eating small portions at regular intervals can also help by reducing the workload on the stomach. Understanding your body’s **hunger cues** can aid in adhering to a **meal timing** strategy that promotes better digestion and prevents overwhelming the digestive system.
Meal Suggestions for Better Digestion
To optimize your **gastroparesis diet**, consider these **meal suggestions**: breakfast could include a **fruit smoothie** made with yogurt and berries; lunch may consist of a blended vegetable soup paired with whole grains; and dinner could focus on soft proteins like baked chicken breast served with mashed potatoes. All meals should prioritize **portion control** and individual preferences to ensure compliance and enhance the effectiveness of the therapeutic eating patterns. Remember to include **electrolyte balance** by staying hydrated and choosing drinks that contribute positively to overall nutrition.
Implementing Dietary Strategies
Adopting a supportive diet involves not only selecting appropriate foods but also employing effective cooking methods and **food preparation techniques**. People with gastroparesis often benefit from avoiding high-fat and high-fiber options while focusing on simpler meals that require minimal digestion effort. Cooking methods such as steaming, boiling, or slow cooking can help create **comfort foods** that are easy on the stomach. It’s also valuable to monitor individual food reactions through **food diaries**, which can identify personal triggers and uphold dietary adjustments that promote **digestive wellness**.
Incorporating Snacks into Your Diet
Strategic snacking intervals are crucial for maintaining stable energy levels and managing hunger throughout the day. Emphasizing **snacking options** that are **easy-to-digest foods**, like plain yogurt or creamy peanut butter on soft bread, can also prevent excessive hunger cues from arising. Knowing the best times to include snacks around meal times can help establish **healthy eating patterns** that support good health while reducing symptoms of distress. Evaluating and incorporating **digestive aids** can also complement these snacks, promoting better absorption of essential nutrients.
Emotional and Psychological Considerations in Dietary Adjustments
Changing eating behaviors and practices can evoke emotional responses, especially when dealing with chronic conditions like gastroparesis. Be proactive in practicing **mindful eating** and focusing on **satiety signals** to adjust your meal frequency effectively. Additionally, consider including **cooking innovations** that replace foods that are difficult to digest with alternatives that provide similar satisfaction but are physically easier to manage. Engaging in emotional self-care strategies may also support better adherence and enhance general **wellness outcomes** linked to your personalized dietary plan.
The Importance of Professional Guidance
Working with a registered dietitian can make a substantial difference in optimizing your **nutrition management**. Seeking **dietitian advice** ensures adherence to individualized nutrition based on your unique requirements and preferences. They can help tailor your **dietary adjustments**, instruct you on **food tracking**, and suggest appropriate **dietary supplements** where necessary. This professional insight plays a strategic role in managing **symptoms**, allowing you to navigate **grocery shopping tips** and offer meal variety tailored to your specific needs.
Embracing Lifestyle Changes for Improved Gastrointestinal Health
Improving **gastrointestinal motility** often calls for incorporating holistic shifts in lifestyle around the **gastroparesis diet**. Factors like physical activity, managing stress, and long-term goal setting can empower personal health journeys. Consider introducing yoga or light physical activity if comfortable, as it can improve digestion and overall well-being. Also, learning new **cooking techniques** can enhance your food experience and provide engaging ways to prepare meals that suit your dietary restrictions while remaining enjoyable.
Cooking Methods for Digestive Ease
Experimenting with different **cooking methods** can greatly impact the comfort of your meals. Keep an eye on how food is prepared when planning meals to maintain **nutrient absorption** and allow them to be more easily digested. Some favorable options are steaming and boiling, compared to frying, which can add unnecessary fat and calories. Also, opt for **medicinal foods** and ingredients known for their anti-inflammatory properties, helping not just with digestion but also overall **nutritional wellness**.
Advocating Your Needs with Dining Out
Dining out can present challenges for those managing a **gastroparesis diet**. Researching restaurants ahead of time and honing in on menu items that align well with **food texture** preferences and portion control can significantly enhance the experience. Making dietary inquiries helps ensure proper customizations are in place, such as requesting modifications to food choices that are softer or more hydrating. Don’t hesitate to communicate your needs, as many establishments are willing to accommodate dietary restrictions.
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Expectations
Staying attuned to personal progress and setbacks is essential in managing a **gastroparesis meal plan** successfully. Through conscious **food tracking**, individuals can identify patterns that correlate with symptom relief or aggravation. This self-monitoring leads to a dynamic and adaptable dietary framework that makes necessary adjustments a regular practice. Bolstering support with **educational resources** and remaining flexible in meal choices will allow individuals to associate positive health outcomes with their efforts.
Key Takeaways
- Focus on small, frequent meals featuring low-fiber, easy-to-digest foods ideal for managing symptoms.
- Incorporate a variety of textures, cooking methods, and nutrient profiles to maintain dietary diversity.
- Work with a dietitian for tailored advice, meal tracking, and supplement recommendations.
- Adapting cooking techniques and practicing mindful eating can spark enjoyment in meal preparation.
- Be proactive in seeking resources and education to enhance dietary adherence for optimal digestive health.
FAQ
1. What are the best snack options for a gastroparesis diet?
Great snacks under a **gastroparesis diet** include options like smoothies, yogurt, soft cheese, or blended vegetable dips paired with soft bread or crackers. These snacks are easier to digest and can be integrated into consistent meal timings.
2. How can I track my food intake effectively on this diet?
Using a **food diary** can significantly aid in monitoring food choices and their effects on your symptoms. Consider using apps for meal tracking that gauge nutrients and dietary patterns for better self-awareness and **nutritional adherence**.
3. Are there specific cooking methods recommended for digestion?
Yes, cooking techniques like steaming, boiling, or slow cooking soften food textures making them easier to digest. Avoid frying as it adds excess fat that can aggravate symptoms.
4. What type of fruits are best to include in the diet?
Opt for **soft fruits** such as ripe bananas, applesauce, or well-cooked fruits preserved without added sugars to ease potential digestive discomfort while providing vital nutrients.
5. Can stress affect my digestive health?
Absolutely. Stress has direct effects on **digestive health**, and continuing to engage in self-care and mindfulness routines can help manage symptoms and overall wellness better.
6. How important is hydration for those with gastroparesis?
Hydration plays a critical role in **nutrient absorption** and digestive processes, making it fundamental to maintain it through liquids and hydrating foods like soups and broths as part of your **meal prep**.
7. Should I consider dietary supplements, and why?
**Dietary supplements** can be beneficial to ensure you’re meeting your nutritional requirements fully, especially if specific food groups are limited in the diet to prevent deficiencies.